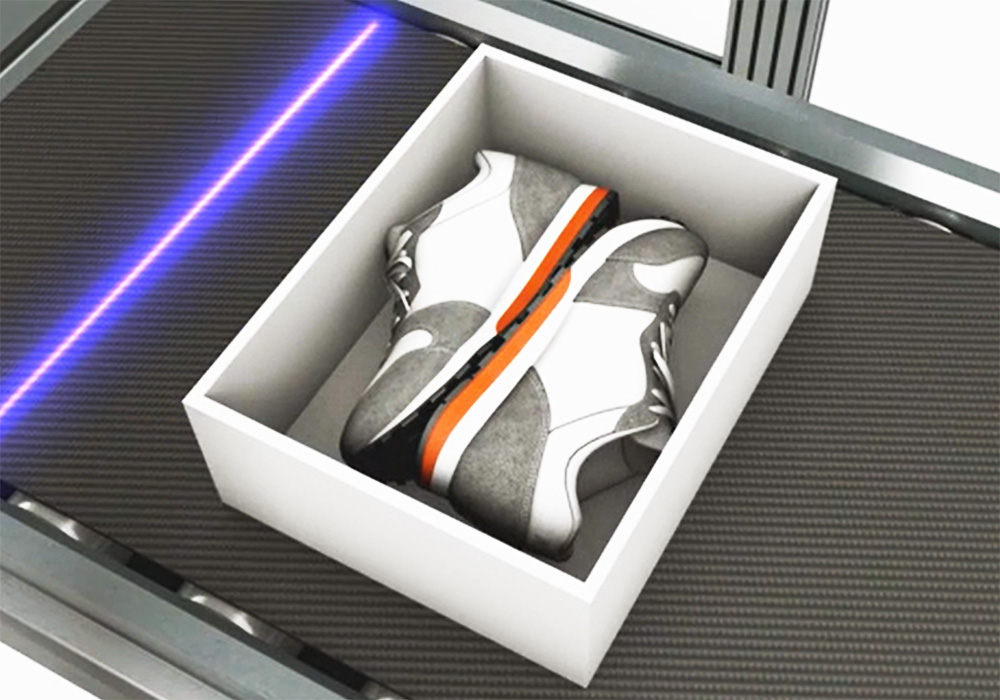
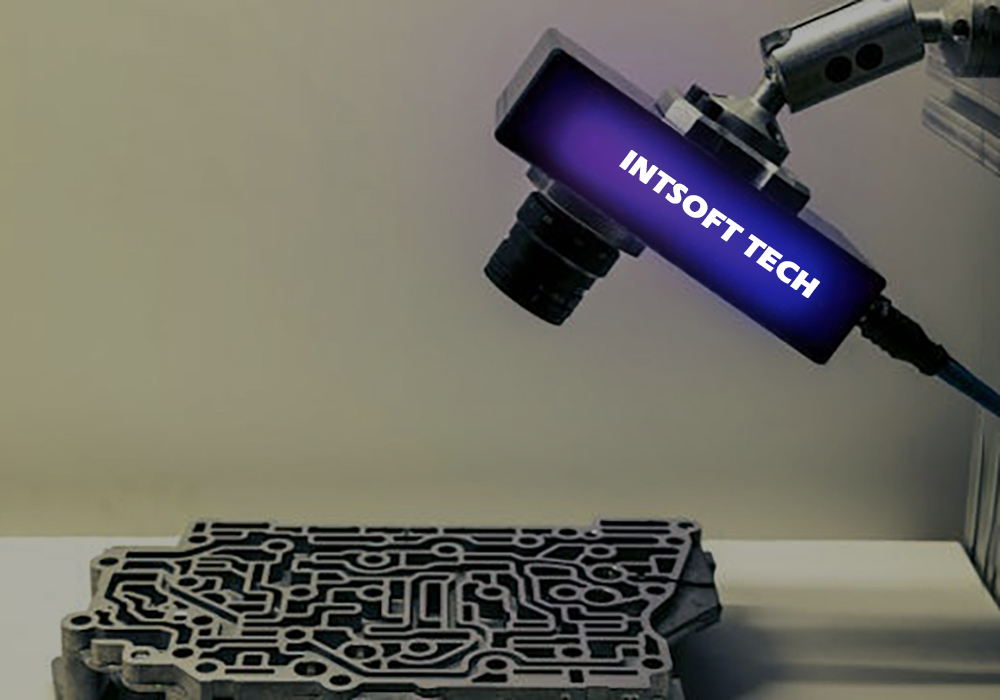
Machine vision is primarily focused on solving specific visual problems, such as identifying objects, detecting defects, or tracking movements in images and videos. It is often used in industrial and manufacturing settings, where it helps automate tasks such as quality control or robotic guidance. Machine vision systems are designed to perform these specialized visual tasks by using techniques such as image processing, pattern recognition, and computer vision. They are usually programmed by humans to perform predefined functions, and they have a relatively limited range of capabilities.
By contrast, AI is a much broader and more ambitious field that aims to create systems that can think, learn, and make decisions in a way that mimics or even surpass human intelligence. AI systems are designed to address a wide range of issues, from language understanding and generation to strategic decision-making and creative problem-solving. They use advanced technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing to gain knowledge and skills, often by analyzing large datasets. Unlike machine vision systems, AI systems are designed to be more autonomous and adaptable, able to learn and evolve on their own to cope with new challenges and situations.
While machine vision is focused on specific visual tasks, AI systems can work with various types of data, including text, speech, and sensory information, and can combine multiple cognitive abilities to tackle complex problems. For example, an AI system might use computer vision to analyze images, natural language processing to understand instructions, and machine learning to plan and execute actions. This flexibility and versatility is a key distinction between machine vision and AI.
Another important difference is the level of human involvement. Machine vision systems are typically programmed and configured by human experts to perform their pre-defined functions. In contrast, many modern AI systems are designed to learn and adapt on their own, with less direct human intervention. This allows AI systems to potentially discover new solutions and approaches that may not have been anticipated by their creators.
As you can see from the above description, machine vision is a specialized field focused on solving visual problems, while AI is a broader and more ambitious field that aims to create systems with general intelligence and adaptability. While machine vision and AI share some underlying technologies, such as computer vision and pattern recognition, the scope, complexity, and autonomy of AI systems set them apart from more narrowly focused machine vision applications.