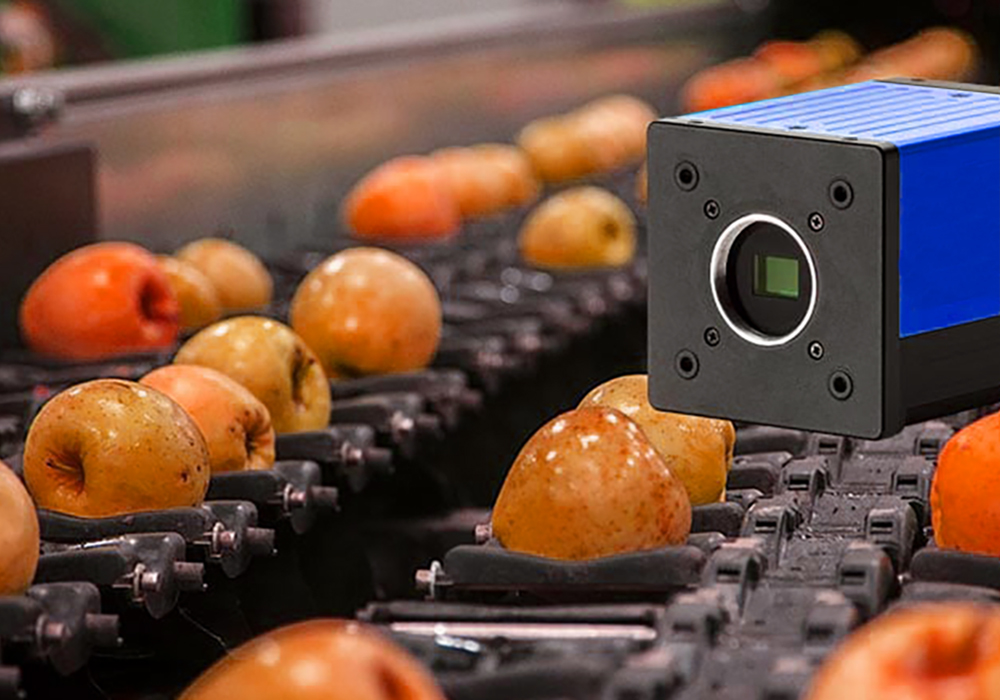
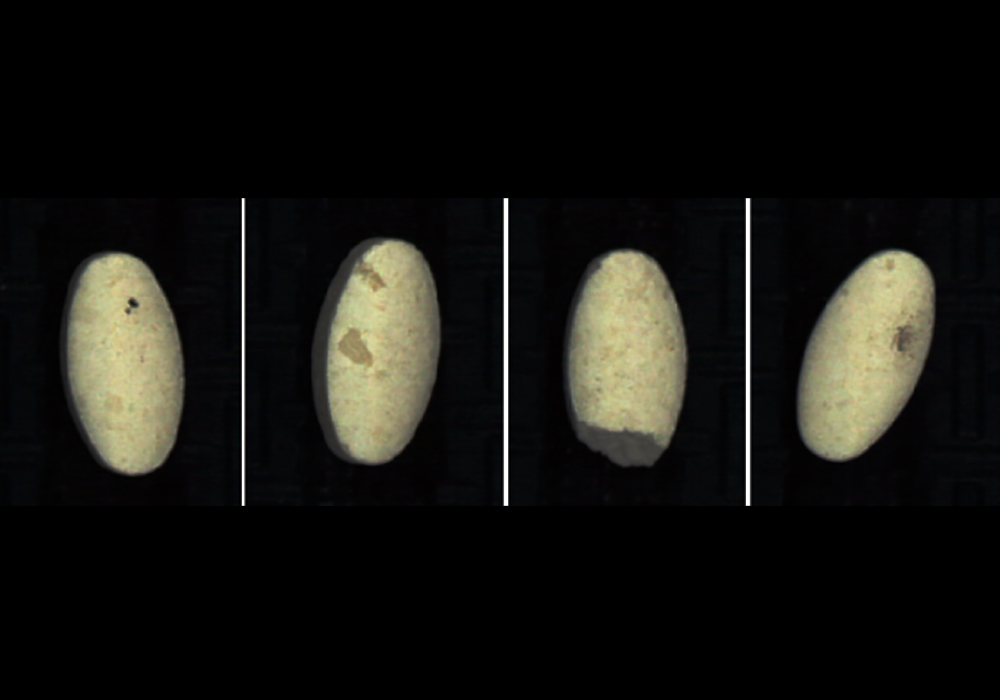
Machine vision systems are relative to human vision systems. In simple terms, it uses industrial cameras (equivalent to human eyes) to capture images of objects, and then processes the images through algorithms (equivalent to human brains) to make judgments about objects. For example, a pile of apples, you can tell which one is of good quality and which one is bad by appearance. If you use human eyes to detect, you judge by color, shape, and other characteristics, which are relatively inefficient and have a high error rate. If you use machine vision systems to detect, you take pictures of apples, and then analyze the photos to get various information about apples.

The machine vision system usually consists of the following devices:
1. Industrial camera: used to capture images.
2. Light source: used to illuminate the detected object so that the industrial camera can capture images that are easier to detect
3. Image processing software: used to enhance the captured image, highlight the characteristics of the image, and make it easier for the next step to judge the image.
4. Machine deep learning model: The model trained by machine deep learning accumulates and analyzes image data previously detected. Just like the way the human brain learns, the more images detected, the more accurate the detection of the next image.
5. Hardware system: A carrier that can run software and models, usually an industrial computer.