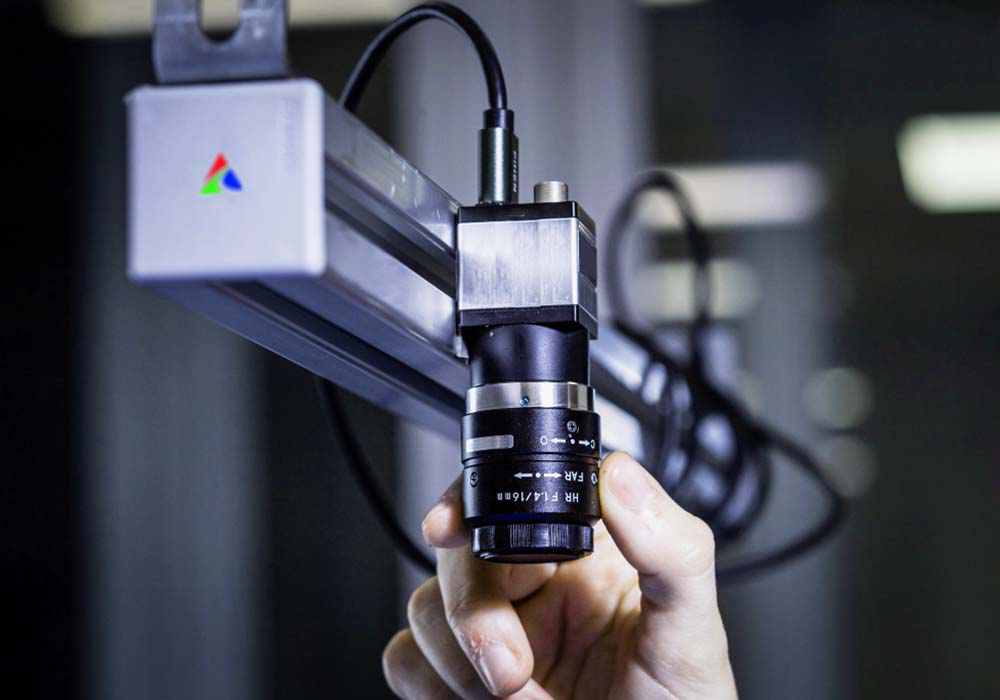
There are generally four main types of visual inspection methods used in industrial and manufacturing settings:
Manual Visual Inspection:

This is the most basic form of visual inspection, where trained human inspectors visually inspect products or components for defects. It relies on the skills and experience of inspectors.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI):

AOI systems use high-resolution cameras and computer vision algorithms to automatically detect and identify defects in products. This is a highly accurate and efficient method compared to manual inspection.
Machine Vision Inspection:
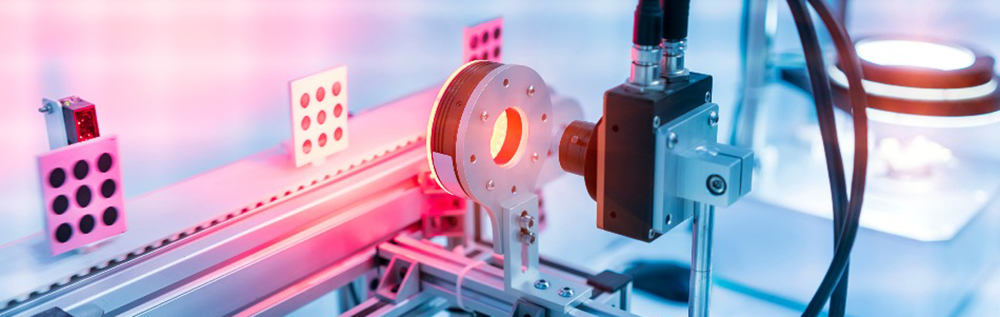
Machine vision systems go beyond simple defect detection. They use advanced image processing, pattern recognition, and artificial intelligence techniques to perform more complex inspections, measurements, and quality assessments.
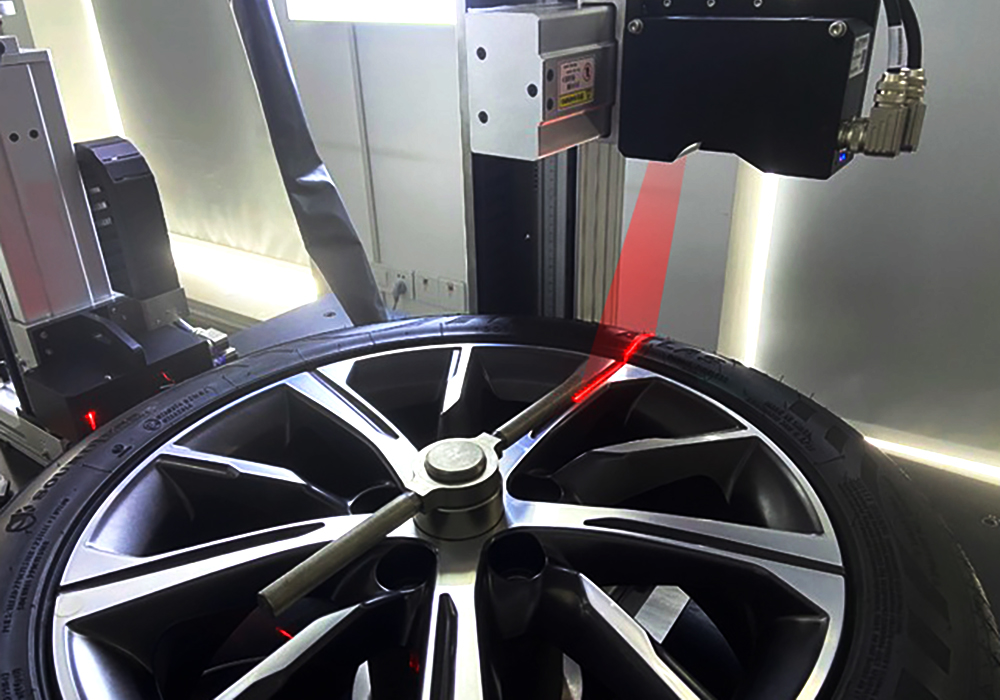
3D Vision Inspection:

This method uses 3D imaging technologies such as laser scanning or structured light to capture detailed 3D models of products. It allows for more comprehensive inspection of complex shapes, dimensions, and surface features that 2D imaging may miss.
The choice of visual inspection method depends on factors such as product complexity, required inspection speed, accuracy requirements, and available budget. Many modern factories employ a combination of these techniques to achieve the desired quality control and manufacturing efficiency.
Key benefits of these advanced visual inspection methods over manual inspection include speed, consistency, objectivity, and the ability to handle large inspection volumes. They play a critical role in driving quality, productivity and automation in today’s smart manufacturing environments.